Introduction
As financial crime becomes more sophisticated, organizations must adopt proactive measures to protect themselves and ensure compliance with stringent regulatory requirements. One such measure is Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD), a crucial component of Anti-Money Laundering (AML) strategies. EDD goes beyond standard due diligence, requiring a more in-depth investigation of high-risk clients and transactions to prevent financial crimes like money laundering and terrorist financing.
This blog explores what EDD is, its role in AML, and how businesses in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) can implement it effectively to meet regulatory expectations.
What is Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD)?
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) is an extended form of due diligence that requires businesses to conduct a more thorough examination of their clients’ profiles and transactions. Unlike standard due diligence, which is applied to all clients, EDD is reserved for clients that pose higher risks, such as Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs), clients from high-risk jurisdictions, or those involved in complex or unusually large transactions.
EDD involves gathering more detailed information, verifying the source of wealth and funds, and maintaining a heightened level of monitoring to identify and mitigate risks associated with high-risk clients. The primary goal of EDD is to ensure that businesses have a comprehensive understanding of their clients and can proactively prevent financial crimes.
Key Differences Between Standard Due Diligence and Enhanced Due Diligence
1. Level of Scrutiny
Standard due diligence involves collecting basic information about the client, such as identification documents, proof of address, and information about the nature of the business relationship. In contrast, EDD requires a deeper investigation, including additional documentation, background checks, and verification of the source of wealth and source of funds.
2. Monitoring Frequency
EDD requires ongoing and enhanced monitoring of transactions. High-risk clients must be monitored continuously to identify any suspicious behavior or changes in their risk profile. This differs from standard due diligence, where monitoring may occur periodically.
3. Documentation Requirements
EDD involves maintaining detailed records of all due diligence activities, including the steps taken to verify information, the source of funds, and the findings from ongoing monitoring. These records must be available for review by regulatory authorities and are essential for demonstrating compliance.
The Importance of Enhanced Due Diligence in AML
1. Regulatory Compliance
EDD is a critical aspect of complying with AML/Counter-Terrorist Financing (CTF) regulations, particularly those set by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF). The UAE, as a member of the FATF, has implemented stringent regulations to combat money laundering and terrorist financing. Businesses that fail to conduct EDD on high-risk clients may face significant fines, regulatory penalties, and reputational damage.
Learn more about AML compliance requirements through our AML Compliance Services.
2. Risk Mitigation
EDD helps businesses identify potential risks associated with high-risk clients and transactions. By thoroughly understanding the client’s background, business activities, and financial dealings, companies can take proactive measures to mitigate the risk of being involved in financial crimes. EDD is particularly effective in identifying red flags, such as clients with a history of adverse media or complex corporate structures designed to obscure ownership.
3. Protecting Business Reputation
Businesses that fail to conduct proper EDD risk being associated with clients involved in illegal activities, such as money laundering or terrorist financing. This can lead to reputational damage, loss of customer trust, and negative media coverage. By conducting thorough EDD, businesses can protect their reputation and demonstrate their commitment to compliance and ethical practices.
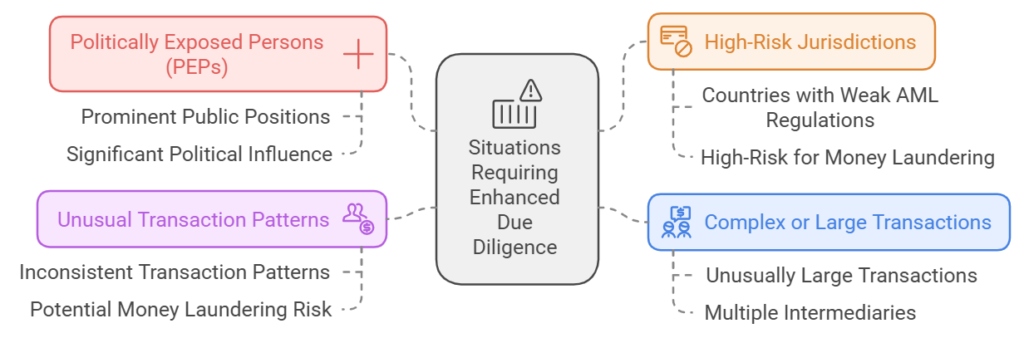
When is Enhanced Due Diligence Required?
EDD is required for clients and transactions that pose a higher risk of money laundering or terrorist financing. Situations that may require EDD include:
- Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs): Individuals who hold prominent public positions or have significant political influence are considered high-risk due to their potential exposure to bribery and corruption.
- High-Risk Jurisdictions: Clients or transactions involving countries that are considered high-risk for money laundering or have weak AML regulations require EDD.
- Complex or Large Transactions: Unusually large transactions or those involving multiple intermediaries may require enhanced scrutiny to ensure that they are legitimate.
- Unusual Transaction Patterns: Clients with unusual or inconsistent transaction patterns may also require EDD to determine if there is a risk of money laundering.
Key Steps in the Enhanced Due Diligence Process
1. Customer Identification and Verification
The first step in the EDD process is identifying and verifying the customer’s identity. Unlike standard due diligence, EDD requires additional verification documents, such as multiple forms of identification, proof of address, and detailed information about the client’s business activities.
2. Assessing the Source of Wealth and Funds
One of the critical components of EDD is determining the source of wealth and source of funds. This involves gathering documentation that provides evidence of how the client obtained their wealth or the origin of the funds being used in a particular transaction. Assessing the source of wealth helps businesses determine if the funds are legitimate or if there are any red flags that require further investigation.
3. Ongoing Monitoring of Transactions
EDD is not a one-time process; it requires continuous monitoring of customer transactions to identify any suspicious activities or changes in behavior. Businesses must implement transaction monitoring systems that can detect unusual activities in real-time, such as large cash transactions, multiple smaller transactions, or cross-border transfers.
For more information on transaction monitoring, explore our Transaction Monitoring Services.
4. Background Checks and Screening
Conducting comprehensive background checks is another essential step in the EDD process. This involves screening clients against international sanctions lists, PEP lists, and databases of adverse media reports. The goal is to identify any negative information that may indicate a higher risk of financial crime.
5. Enhanced Risk Assessment
For high-risk clients, businesses must conduct an enhanced risk assessment to determine the appropriate level of scrutiny. This involves analyzing the customer’s risk factors, including geographic risk, industry risk, and transaction risk. By categorizing clients based on their risk level, businesses can allocate their resources efficiently and focus on clients that pose the highest risk.
Challenges in Conducting Enhanced Due Diligence
1. Complexity of Data Collection
One of the primary challenges of conducting EDD is the complexity involved in collecting and verifying detailed information about high-risk clients. The documentation required for verifying the source of wealth, ownership structures, and other factors can be extensive and time-consuming.
2. Limited Access to Information
In some cases, businesses may face challenges in accessing accurate information, particularly for clients from jurisdictions with limited transparency or inadequate regulatory frameworks. It is important for businesses to leverage third-party databases and verification tools to overcome these challenges and ensure that they have reliable information.
3. High Costs and Resource Allocation
EDD can be resource-intensive, requiring additional time, effort, and financial resources. Businesses need to allocate sufficient resources for conducting in-depth investigations, ongoing monitoring, and documentation. Despite the costs, EDD is necessary to mitigate potential financial and reputational risks.
Best Practices for Effective Enhanced Due Diligence
1. Utilize Advanced Technology for Monitoring
Leveraging advanced technology can significantly enhance the effectiveness of EDD. Automated monitoring tools, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning can help detect unusual patterns and potential risks more accurately and efficiently than manual processes.
2. Train Staff on EDD Requirements
Employees responsible for conducting EDD must be well-trained on regulatory requirements, red flags, and best practices. Regular training ensures that employees are well-equipped to identify suspicious activities, gather the necessary documentation, and follow the correct procedures.
Explore our AML Compliance Training Services for comprehensive training programs on EDD and AML compliance.
3. Engage External Compliance Experts
For businesses that lack the expertise or resources to conduct EDD effectively, engaging external compliance experts can be beneficial. Experienced consultants can provide the necessary guidance and support to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
4. Develop a Risk-Based Approach
Adopting a risk-based approach to EDD allows businesses to focus their resources on the clients and transactions that pose the highest risks. By categorizing customers based on their risk profiles, businesses can prioritize their efforts and take appropriate actions to mitigate potential risks.
How CAMC Can Assist with Enhanced Due Diligence
Chartered AML Consultants (CAMC) provides comprehensive EDD services to help businesses comply with UAE regulations and mitigate financial crime risks. Our services include:
1. EDD Policy Development
We assist businesses in developing EDD policies that align with regulatory requirements and international best practices. Our policies cover all aspects of customer identification, verification, risk assessment, and ongoing monitoring.
2. Background Screening and Verification
Our team conducts thorough background checks and verification of customer information to ensure compliance with regulatory standards. We use advanced tools to screen clients against sanctions lists, PEP lists, and adverse media databases.
3. Source of Wealth Verification
We provide assistance in verifying the source of wealth and funds, ensuring that businesses have reliable and accurate information about their high-risk clients. Our team works closely with clients to gather the necessary documentation and conduct in-depth investigations.
4. Ongoing Monitoring and Reporting
Our ongoing monitoring services help businesses keep track of high-risk clients and transactions. We provide regular updates, risk assessments, and support to ensure that businesses remain compliant with AML regulations.
Conclusion
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) is an essential component of AML compliance for businesses operating in the UAE. It provides a deeper level of scrutiny for high-risk clients, helping businesses mitigate financial crime risks, comply with regulatory requirements, and protect their reputation. By understanding the EDD process, implementing best practices, and leveraging expert support, businesses can effectively manage the risks associated with high-risk clients and ensure compliance with the UAE’s stringent AML regulations.
Partnering with CAMC can make the EDD process more efficient and effective. Our team of experts provides tailored EDD services to help businesses navigate the complexities of AML compliance and achieve their compliance objectives.
For more information on how CAMC can assist with enhanced due diligence, contact us today.
References
Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) – AML Guidance
https://www.fca.org.uk/firms/financial-crime/aml
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime – Anti-Money Laundering
https://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/money-laundering/index.html
OECD – Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs) in AML
https://www.oecd.org/corruption/anti-bribery/PEPs-in-AML
Basel Institute on Governance – AML Index




